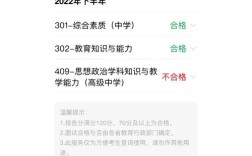
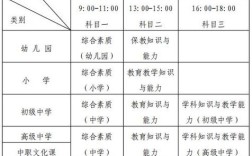
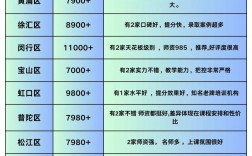
,主要围绕简单句的基本结构展开,包括肯定句、否定句、一般疑问句及其回答、特殊疑问句等,对于三年级学生来说,句型转换的难度较低,主要掌握be动词(am/is/are)、情态动词can、以及have/has的基本用法,通过简单的规则变化即可完成转换,以下从不同句型转换类型、具体方法、注意事项及练习建议等方面进行详细说明。

be动词句型转换
be动词(am/is/are)是英语中最基础的动词,三年级主要掌握第一人称单数(I)用am,第三人称单数(he/she/it)用is,其他人称(you/we/they)用are,句型转换围绕be动词展开,包括肯定句变否定句、一般疑问句及其回答。
肯定句变否定句
规则:在be动词后直接加上not,其余部分不变,缩写形式为am not(无缩写)、is not→isn't、are not→aren't。
示例:
- 肯定句:I am a student.
否定句:I am not a student.(或I'm not a student.) - 肯定句:She is my friend.
否定句:She isn't my friend. - 肯定句:They are in the classroom.
否定句:They aren't in the classroom.
肯定句变一般疑问句及其回答
规则:将be动词提到句首,首字母大写,句尾用问号,人称和be动词相应变化(如I→you,we→you等),回答时用Yes/No,加上人称和be动词。
示例:
- 肯定句:He is tall.
一般疑问句:Is he tall?
肯定回答:Yes, he is. 否定回答:No, he isn't. - 肯定句:We are happy.
一般疑问句:Are you happy?
肯定回答:Yes, we are. 否定回答:No, we aren't.
情态动词can句型转换
can是三年级常见的情态动词,表示“能、会”,后接动词原形,没有人称和数的变化。

肯定句变否定句
规则:在can后直接加上not,缩写为can't。
示例:
- 肯定句:I can swim.
否定句:I can't swim. - 肯定句:She can dance.
否定句:She can't dance.
肯定句变一般疑问句及其回答
规则:将can提到句首,首字母大写,句尾用问号,回答时用Yes/No,加上can和人称。
示例:
- 肯定句:Tom can play football.
一般疑问句:Can Tom play football?
肯定回答:Yes, he can. 否定回答:No, he can't. - 肯定句:They can sing English songs.
一般疑问句:Can they sing English songs?
肯定回答:Yes, they can. 否定回答:No, they can't.
have/has句型转换
have/has表示“有”,第三人称单数(he/she/it)用has,其他人称用have。
肯定句变否定句
规则:在have/has后加上not,have not→haven't,has not→hasn't。
示例:

- 肯定句:I have a dog.
否定句:I haven't a dog.(或I don't have a dog.,三年级主要掌握haven't/hasn't) - 肯定句:She has a new book.
否定句:She hasn't a new book.
肯定句变一般疑问句及其回答
规则:将have/has提到句首,首字母大写,句尾用问号,回答时用Yes/No,加上have/has和人称。
示例:
- 肯定句:We have many friends.
一般疑问句:Have you many friends?
肯定回答:Yes, we have. 否定回答:No, we haven't. - 肯定句:He has a red bike.
一般疑问句:Has he a red bike?
肯定回答:Yes, he has. 否定回答:No, he hasn't.
特殊疑问句句型转换
特殊疑问句用来询问特定信息,由“特殊疑问词+一般疑问句”构成,三年级常见的特殊疑问词有:what(什么)、where(哪里)、who(谁)、how old(多大)、what colour(什么颜色)等。
特殊疑问词的确定选择合适的疑问词:
- 询问事物/职业:What(如:What's this? / What's your father?)
- 询问地点:Where(如:Where is my pen?)
- 询问年龄:How old(如:How old are you?)
- 询问颜色:What colour(如:What colour is your bag?)
转换方法
规则:用特殊疑问词替换原句中的相应部分,其余部分变为一般疑问句结构(be动词/情态动词提前)。
示例:
- 肯定句:This is a cat.(询问事物)
特殊疑问句:What is this? - 肯定句:My book is on the desk.(询问地点)
特殊疑问句:Where is your book? - 肯定句:He can play the piano.(询问能力)
特殊疑问句:What can he do? - 肯定句:Her hair is long.(询问颜色)
特殊疑问句:What colour is her hair?
句型转换注意事项
- 人称和数的变化:一般疑问句中,人称要与be动词/情态动词/have/has保持一致,如I→you,we→you,he/she/it→it等。
- 缩写形式:否定句中的缩写形式(isn't、aren't、can't、haven't、hasn't)要熟练掌握,注意am not没有缩写形式。
- 标点符号:疑问句句尾必须用问号,肯定句和否定句句尾用句号。
- 大小写:疑问句首字母和专有名词首字母要大写,人称代词I永远大写。
句型转换练习方法
- 分类练习:先集中练习一种句型转换(如be动词变否定句),熟练后再练习其他类型。
- 情景对话:结合生活场景进行句型转换,如描述自己的物品、能力等,增强实用性。
- 错题整理:将易错的句型(如第三人称单数的has/is转换)整理出来,反复练习。
- 游戏互动:通过“句型转换接龙”等游戏,让学生在轻松氛围中巩固知识。
以下为常见句型转换示例表格:
| 原句(肯定句) | 否定句 | 一般疑问句 | 肯定回答 | 否定回答 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I am a teacher. | I am not a teacher. | Are you a teacher? | Yes, I am. | No, I'm not. |
| She is in the park. | She isn't in the park. | Is she in the park? | Yes, she is. | No, she isn't. |
| They can run fast. | They can't run fast. | Can they run fast? | Yes, they can. | No, they can't. |
| He has a blue car. | He hasn't a blue car. | Has he a blue car? | Yes, he has. | No, he hasn't. |
| This is an apple. | This isn't an apple. | What is this? | ||
| My book is on the chair. | My book isn't on the chair. | Where is your book? |
相关问答FAQs
问题1:三年级学生在句型转换中常犯的错误有哪些?如何避免?
解答:常见错误包括:①be动词人称与数不一致(如第三人称单数用are);②否定句中漏加not(如“I am not”写成“I am”);③特殊疑问句中未提前be动词/情态动词(如“What this is?”正确应为“What is this?”),避免方法:通过口诀记忆规则(如“be动词提句首,人称跟着be走变化”),结合大量例句对比练习,错题反复订正。
问题2:如何帮助三年级学生更好地掌握特殊疑问句的转换?
解答:可采用“三步法”:第一步,明确疑问词对应的信息(如where对应地点);第二步,用疑问词替换原句关键词(如“我的书包在桌子上”替换为“Where is my书包?”);第三步,将剩余部分变为一般疑问句(如“is my书包”→“is your书包”),借助图片、实物等直观教具,让学生在具体场景中练习,如指着物品问“What's this?”,增强理解记忆。